Getting Started with the Codex Agent: A Beginner’s Guide for Developers
Life made easy with Codex
If you’re a developer curious about AI coding assistants but not sure where to begin, the Codex Agent is one of the most powerful tools you can add to your workflow. Codex can help you build applications, review code, generate tests, refactor projects, create documentation, and even produce infrastructure as code.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
What Codex actually is (AI agent vs. language model)
How Codex works across the CLI (terminal), IDEs like VS Code and Cursor, and the Cloud (GitHub, ChatGPT web, and mobile)
The different modes of operation
System requirements and setup considerations
Best practices for getting reliable results
Whether you’re a beginner or just exploring AI-powered development for the first time, this article will give you a clear path forward.
You can also follow along in my YouTube masterclass series on OpenAI Codex
What is Codex?
One point of confusion for many developers is that “Codex” refers to two related but distinct things:
Codex the Language Model (LLM):
A specialized version of GPT that has been fine-tuned for software engineering tasks.Codex the AI Agent:
A harness built on top of the model that integrates into your workflow and helps you write, analyze, and manage code.
When you hear people talk about “using Codex,” they’re usually referring to the AI agent or harness, not the raw language model.
Where Can You Use Codex?
Codex is flexible and runs in multiple environments depending on your preference and workflow.
1. Codex in the IDE (VS Code, Cursor, JetBrains)
Works as an extension you can install in Visual Studio Code or forks like Cursor and Windsurf. JetBrains also has a marketplace extension that allows you to configure it for the IDEs like Intellij
Lets you chat with Codex about your code, ask it to make edits, or even let it run autonomously in “YOLO” mode.
Great for developers who spend most of their day inside an IDE.
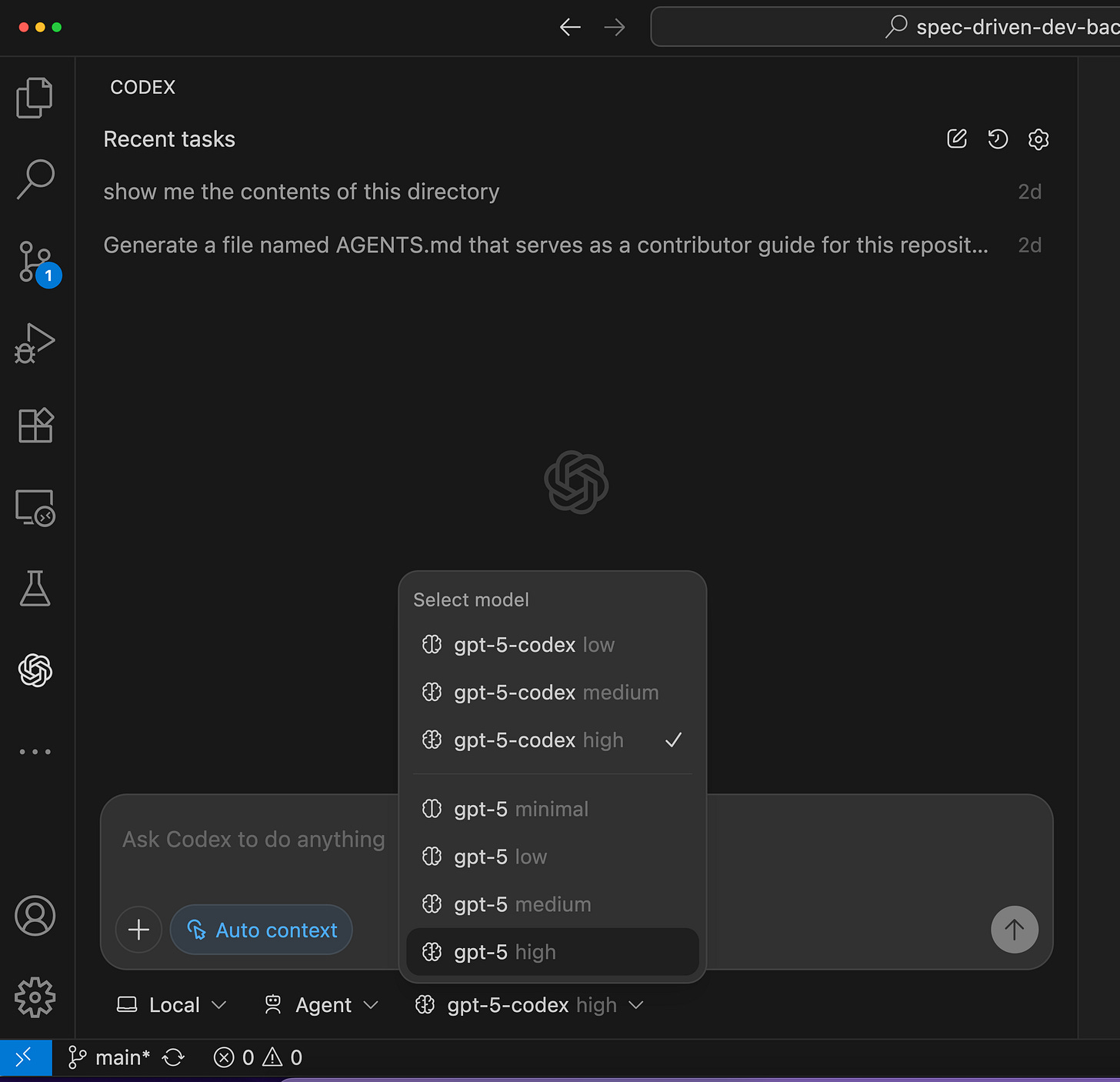
2. Codex in the CLI (Terminal)
Install Codex as a command-line tool and run it directly from your terminal.
Type
codexand interact with it just like any other CLI program.You can specify which model to use, making it ideal for quick coding tasks, file generation, or automation.
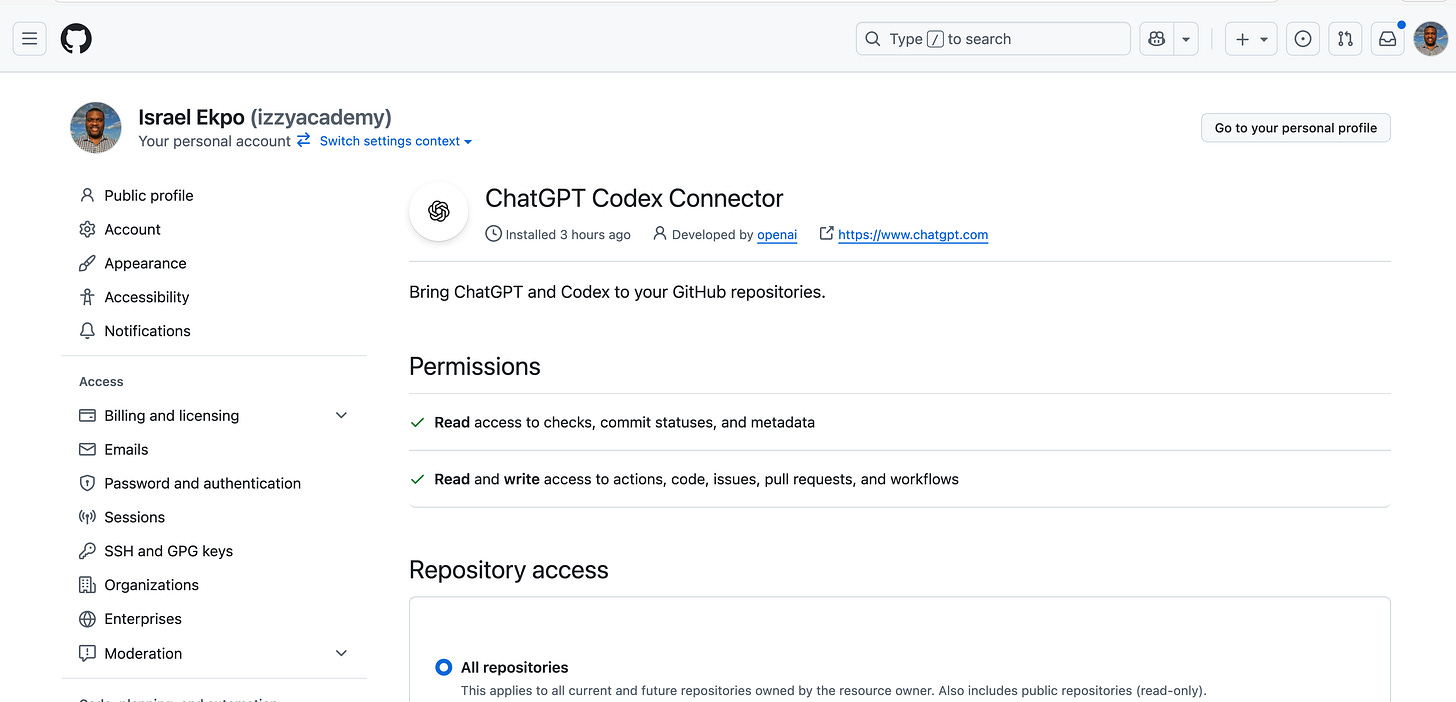
3. Codex in the Cloud
Use Codex in GitHub for automated code reviews and pull request suggestions.
Access it in ChatGPT web or mobile apps for on-the-go coding help.
Run tasks asynchronously in the background or integrate it into your DevOps pipeline.
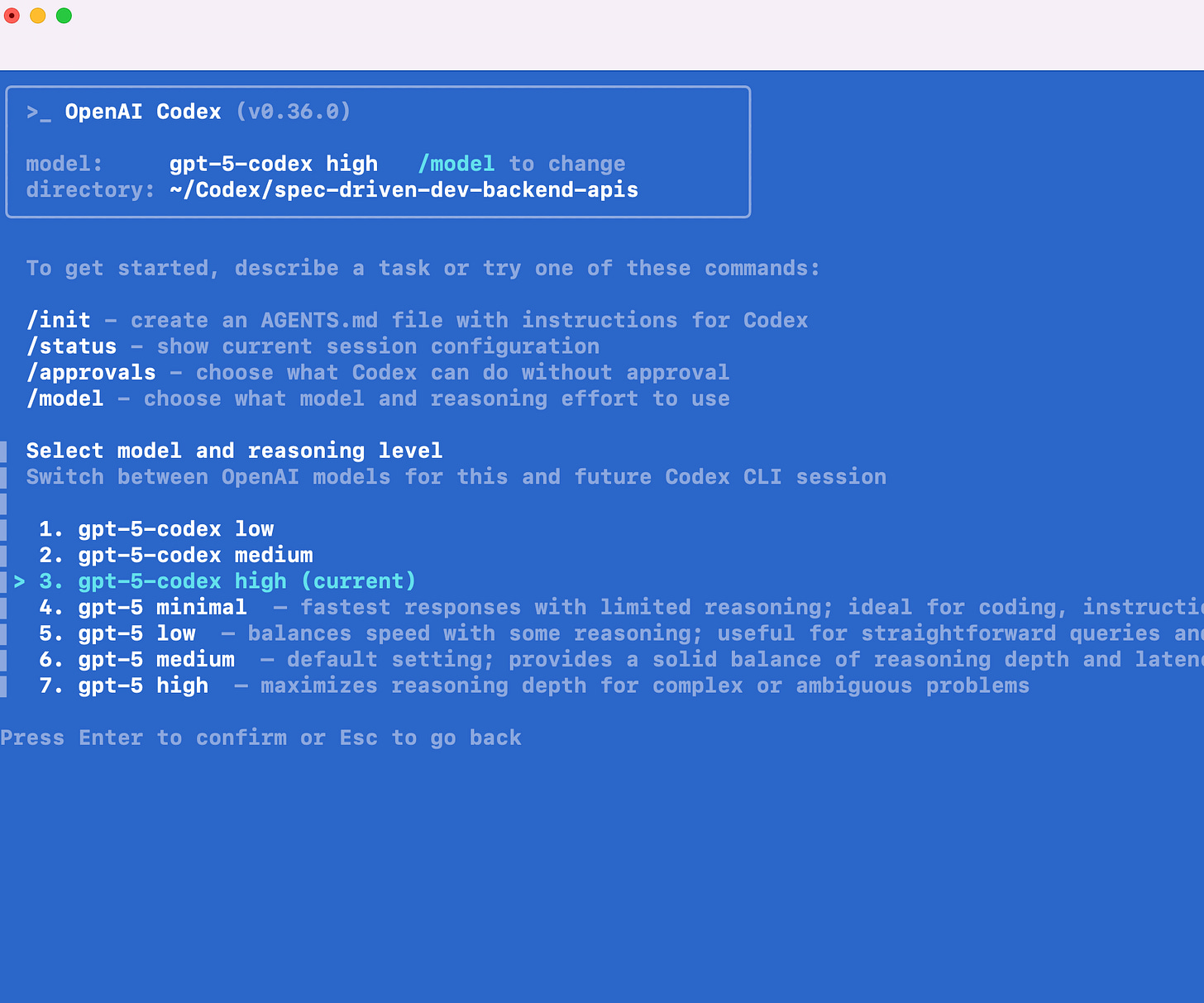
Modes of Operation for Codex IDE Agent
Codex isn’t one-size-fits-all. It has different modes depending on how much control you want to give it:
Chat Mode: Codex gives advice and analysis but does not make edits.
Agent Mode: Codex can create and edit files, with your approval.
YOLO Mode: Codex has full access to your workspace and can edit freely without asking.
Choose your mode carefully based on your trust level and the task at hand.
Key Factors That Influence Codex Results
Your success with Codex depends on three things working together:
You, the Developer:
Your domain knowledge, problem-solving skills, and ability to give clear instructions.The Language Model:
Different models have different capabilities, latencies, and costs. GPT-5 Codex is recommended for most developers.The Harness (Agent Implementation):
The way Codex is configured, whether in IDE, CLI, or cloud, shapes how effective it is in your workflow.
Best Practices for Developers Using Codex
Set up testing and linting: Codex relies on your environment to validate its outputs.
Use AGENTS.md and PLAN.md files: Guide Codex on tasks and expectations for consistent results.
Organize repositories by concern: Prevent confusion and improve agent accuracy.
Enable search features: Ensure Codex can access the latest context and dependencies.
Start small: Use Chat Mode first before moving to more autonomous modes.
System Requirements for CLI and IDE Extension
Codex can run on modest hardware, but for smooth performance:
Minimum: 4 GB RAM
Recommended: 8–16 GB RAM (especially when working with large files or projects)
Why Codex Matters for Developers
Codex is more than just an autocomplete tool. It can act as a coding partner, guiding you through specification-driven development, helping you scaffold projects, writing unit tests, and even generating Terraform scripts or SQL queries.
By mastering Codex in the IDE, CLI, and Cloud, you’ll position yourself to work faster, reduce repetitive tasks, and focus on higher-level problem-solving.
Next Steps
Ready to try Codex? Start by:
Installing the extension in VS Code or Cursor.
Testing it in the CLI for small tasks.
Connecting it to your GitHub repo for automated code reviews.
And if you’d like hands-on tutorials and project examples, join my newsletter for updates, resources, and upcoming Codex challenges:
👉 Subscribe here: